JUC-ReentrantLock实现原理
发表于更新于
字数总计:1.8k阅读时长:7分钟 上海
ReentrantLock 深度剖析
ReentrantLock 是 JUC 包中最重要的锁实现,理解其原理对于掌握 Java 并发编程至关重要。
一、ReentrantLock 概述
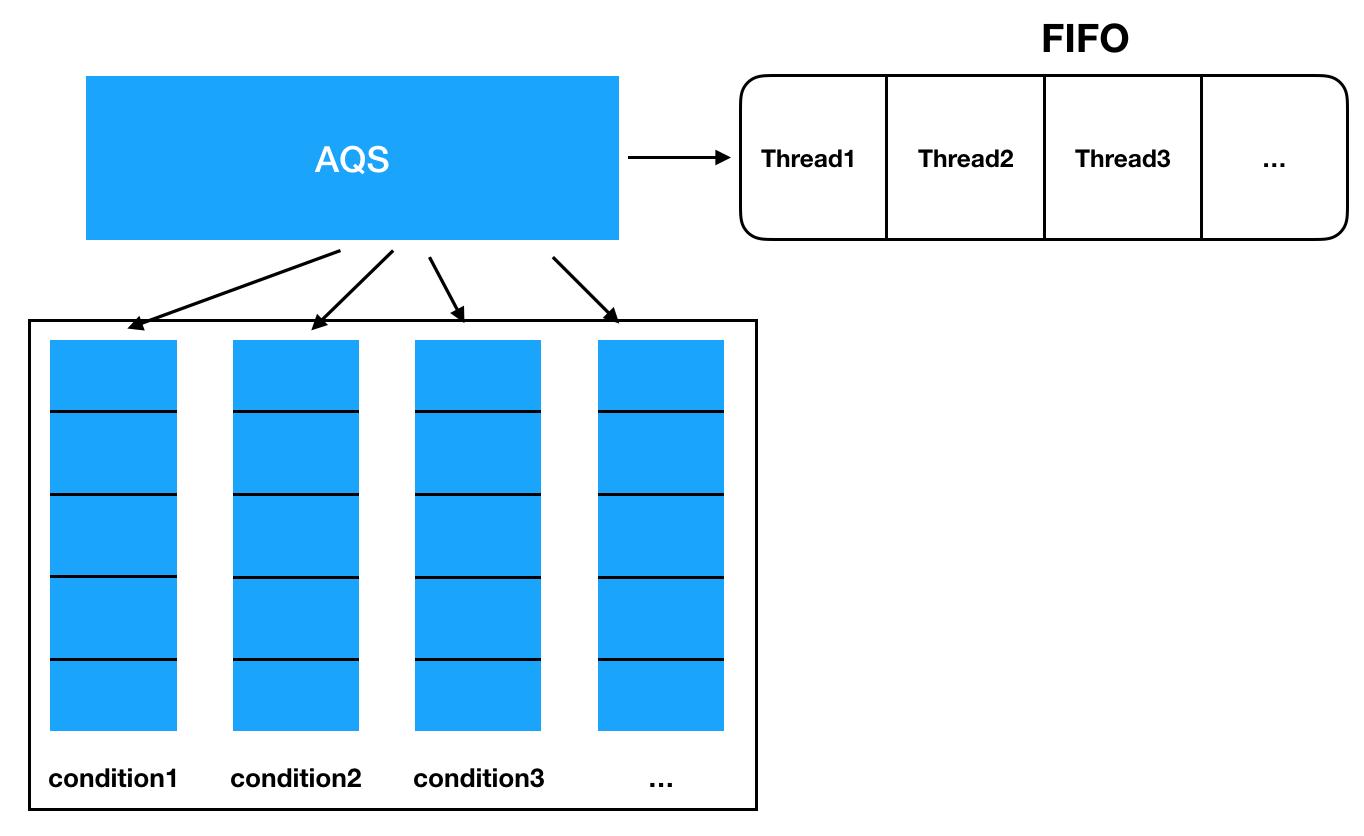
ReentrantLock 是基于 AQS(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer)实现的可重入独占锁,相比 synchronized 提供了更丰富的功能特性。
1.1 核心特性
| 特性 | 说明 |
|---|
| 可重入 | 同一线程可多次获取锁,通过 state 计数器实现 |
| 公平/非公平 | 可选择按 FIFO 顺序获取锁或允许插队 |
| 可中断 | 支持 lockInterruptibly() 响应中断 |
| 超时获取 | 支持 tryLock(timeout) 限时等待 |
| 多条件变量 | 支持多个 Condition 队列 |
1.2 内部结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
private final Sync sync;
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
}
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
}
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
}
}
|
依赖的核心组件:
state 变量:表示锁的持有状态和重入次数- 同步队列(CLH 队列):双向链表,存放等待获取锁的线程
- 等待队列(Condition 队列):单向链表,存放调用 await() 的线程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| +-----------+ +-----------+ +-----------+
同步队列: | head | <-> | node1 | <-> | tail |
+-----------+ +-----------+ +-----------+
|
v (signal)
+-----------+ +-----------+
等待队列: | firstWait | --> | lastWait |
+-----------+ +-----------+
|
二、源码深度分析
2.1 加锁流程(以非公平锁为例)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
|
2.2 tryAcquire 实现对比
非公平锁:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
|
公平锁:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
Node t = tail;
Node h = head;
Node s;
return h != t &&
((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());
}
|
2.3 入队与阻塞
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null;
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
|
2.4 解锁流程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
|
三、公平锁 vs 非公平锁
| 对比维度 | 公平锁 | 非公平锁 |
|---|
| 获取顺序 | FIFO,按入队顺序 | 允许插队 |
| 吞吐量 | 较低(频繁切换) | 较高(减少切换) |
| 饥饿问题 | 不会饥饿 | 可能饥饿 |
| 适用场景 | 对公平性要求高 | 追求性能(默认) |
为什么默认是非公平锁?
非公平锁在线程刚释放锁时,新来的线程可能直接获取锁,避免了唤醒队列中线程的开销,减少了线程上下文切换,吞吐量更高。
1
2
3
4
5
|
ReentrantLock fairLock = new ReentrantLock(true);
ReentrantLock unfairLock = new ReentrantLock(false);
|
四、Condition 条件变量
Condition 提供了类似 Object.wait/notify 的功能,但支持多个等待队列。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (count == items.length)
notFull.await();
items[putIndex] = e;
if (++putIndex == items.length) putIndex = 0;
count++;
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (count == 0)
notEmpty.await();
E e = items[takeIndex];
if (++takeIndex == items.length) takeIndex = 0;
count--;
notFull.signal();
return e;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
|
五、CAS 与自旋锁
5.1 CAS 原理
CAS(Compare And Swap)是一种硬件级别的原子操作,底层依赖 CPU 的 cmpxchg 指令。
1
2
3
|
public final native boolean compareAndSwapInt(
Object obj, long offset, int expect, int update);
|
三个操作数:
执行逻辑:若 V == E,则 V = N,返回 true;否则返回 false。
5.2 自旋锁实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class SpinLock {
private final AtomicReference<Thread> owner = new AtomicReference<>();
public void lock() {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
while (!owner.compareAndSet(null, current)) {
Thread.yield();
}
}
public void unlock() {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
owner.compareAndSet(current, null);
}
}
|
自旋锁的优缺点:
| 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|
| 避免线程上下文切换 | 锁饥饿:某线程可能一直抢不到锁 |
| 适合短时间锁持有 | 总线风暴:多核 CAS 同一变量导致缓存一致性开销 |
5.3 AQS 中的自适应自旋
AQS 在 acquireQueued 中会先自旋一定次数再阻塞,自旋次数由 JVM 根据历史成功率动态调整。
六、ReentrantLock vs synchronized
| 特性 | synchronized | ReentrantLock |
|---|
| 实现层面 | JVM 内置 | JDK 实现 |
| 锁获取释放 | 隐式(自动) | 显式(手动) |
| 可中断获取 | 不支持 | lockInterruptibly() |
| 超时获取 | 不支持 | tryLock(timeout) |
| 公平锁 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 条件变量 | 单一 | 多个 Condition |
| 锁状态查询 | 不支持 | isLocked(), getQueueLength() |
| 性能 | JDK 6+ 优化后相当 | 相当 |
七、最佳实践
7.1 标准使用模板
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void doSomething() {
lock.lock();
try {
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
|
7.2 使用 tryLock 避免死锁
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public boolean transferMoney(Account from, Account to, int amount) {
while (true) {
if (from.lock.tryLock()) {
try {
if (to.lock.tryLock()) {
try {
return true;
} finally {
to.lock.unlock();
}
}
} finally {
from.lock.unlock();
}
}
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(10));
}
}
|
7.3 选择建议
- 优先 synchronized:简单场景,JVM 自动优化
- 使用 ReentrantLock:需要可中断、超时、公平锁、多条件变量等高级特性